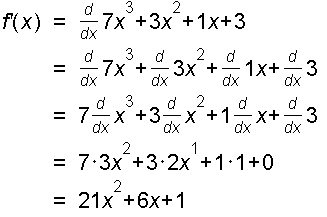![]()
provided this limit exists.
Derivative
Objectives: In this tutorial, using the definition of derivative, we derive a number of elementary differentiation formulas. Some examples are provided to show the use of these formulas. After working through these materials, the student should be able
Modules:
| Definition.
Let y = f(x) be a function. The derivative
of f is the function whose value at x is the limit
provided this limit exists. |
Theorem A. The derivative of a constant is 0.Theorem B. The derivative of the identity function f(x) = x is the constant function f '(x) = 1.
Theorem C. If the function g(x) = k f(x) where k is a constant and f is a differentiable function, then g '(x) = k f '(x).
Theorem D. If f and g are differentiable functions, then (f + g)'(x) = f '(x) + g '(x)
Corollary. If f and g are differentiable functions, then (f - g)'(x) = f '(x) - g '(x)
Theorem E. (Power Rule) If f(x) = xn where n is a positive integer, then f '(x) = n xn - 1
Example 1: f(x) = 3x3 + 6x2 + 2x + 8
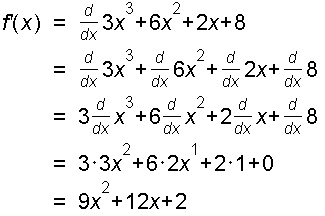
Example 2: f(x) = 8x3 + x2 + 4x + 3
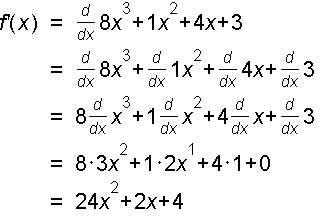
Example 3: f(x) = x3 + 11x2 + 5x + 9
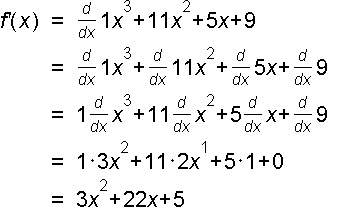
Example 4: f(x) = 7x3 + 3x2 + x + 3