MGS3100: Forecasting & Quality Management
Sample Questions for Exam 2
Consider the time series below with 15 observations. Two types of forecasts are shown – 4 period moving average and Simple Exponential Smoothing with an alpha of 0.5. Fill in the blanks where appropriate and calculate the BIAS, MAD, and Standard Error for both methods.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
alpha= |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
4 period |
|
Abs |
Error |
|
Exponential |
|
Abs |
Error |
|
Period |
Sales |
Average |
Error |
Error |
Squared |
|
Smoothing |
Error |
Error |
Squared |
|
1 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
14.13 |
7.88 |
7.88 |
62.02 |
|
6 |
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
18.06 |
9.94 |
9.94 |
98.75 |
|
7 |
26 |
20.75 |
5.25 |
5.25 |
27.56 |
|
23.03 |
2.97 |
2.97 |
8.81 |
|
8 |
35 |
23.25 |
11.75 |
11.75 |
138.06 |
|
24.52 |
10.48 |
10.48 |
109.92 |
|
9 |
36 |
27.75 |
8.25 |
8.25 |
68.06 |
|
29.76 |
6.24 |
6.24 |
38.96 |
|
10 |
39 |
31.25 |
7.75 |
7.75 |
60.06 |
|
32.88 |
6.12 |
6.12 |
37.47 |
|
11 |
44 |
34.00 |
10.00 |
10.00 |
100.00 |
|
35.94 |
8.06 |
8.06 |
64.97 |
|
12 |
41 |
38.50 |
2.50 |
2.50 |
6.25 |
|
39.97 |
1.03 |
1.03 |
1.06 |
|
13 |
47 |
40.00 |
7.00 |
7.00 |
49.00 |
|
40.48 |
6.52 |
6.52 |
42.45 |
|
14 |
55 |
42.75 |
12.25 |
12.25 |
150.06 |
|
43.74 |
11.26 |
11.26 |
126.73 |
|
15 |
60 |
46.75 |
13.25 |
13.25 |
175.56 |
|
49.37 |
10.63 |
10.63 |
112.97 |
Summarize your computations in the table below.
|
|
BIAS |
MAD |
Standard Error |
|
4 Period Average |
|
|
|
|
Exponential Smoothing |
|
|
|
1. Interpret the BIAS and MAD.
2. Based on the above table, which is the better forecast? Why?
3. Use the better of the two methods to forecast sales for the 16th period.

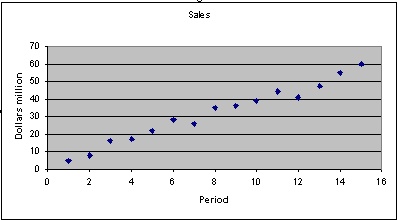
4. Above is a scatter plot of the same data. What method does this indicate as the best one to use for forecasting?
5. Write down the estimated simple regression function (visual estimate) from the above graph.
|
SUMMARY OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Regression Statistics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Multiple R |
0.9882 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R Square |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard Error |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Observations |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANOVA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
df |
SS |
MS |
F |
Significance F |
|
|
|
|
Regression |
1 |
3686.629 |
|
542.736 |
0.000 |
|
|
|
|
Residual |
13 |
88.305 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
14 |
3774.933 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coefficients |
Standard Error |
t Stat |
P-value |
Lower 95% |
Upper 95% |
Lower 95.0% |
Upper 95.0% |
|
Intercept |
2.9048 |
1.4161 |
2.0512 |
0.0610 |
-0.1546 |
5.9641 |
-0.1546 |
5.9641 |
|
Period |
3.6286 |
0.1558 |
23.2967 |
0.0000 |
3.2921 |
3.9651 |
3.2921 |
3.9651 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESIDUAL OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Observation |
Predicted Sales |
Residuals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
6.5333 |
-1.5333 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
10.1619 |
-2.1619 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
13.7905 |
2.2095 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
17.4190 |
-0.4190 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
21.0476 |
0.9524 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
24.6762 |
3.3238 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
28.3048 |
-2.3048 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
31.9333 |
3.0667 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
35.5619 |
0.4381 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
39.1905 |
-0.1905 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
42.8190 |
1.1810 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
46.4476 |
-5.4476 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
50.0762 |
-3.0762 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
53.7048 |
1.2952 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
57.3333 |
2.6667 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consider the regression output shown above for the same data.
6. What is the regression equation?
7. Forecast the sales for period 16.
8. Calculate BIAS, MAD, and Std. Error for the regression.
9. Based on the above criteria, how does this method fare compared to the heuristic methods?
10. Calculate R-squared and interpret the value.
11. Is the regression statistically significant?
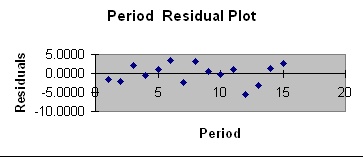
12. Does the Residual plot below suggest that some other regression function must be used instead of the simple linear model?
13. What is a seasonal index? What would a seasonal index of 1.25 mean?
14. Is the BIAS for a forecast using Log Y regression equal to 0?
15. If the forecasted log Y is 6.34, what is the forecasted value of Y?
16. If the forecasted deseasonalized Y for Quarter 1 is 34, what is the forecasted Y for that quarter if the seasonal indices are as follows:
|
Quarter1 |
Quarter2 |
Quarter3 |
Quarter4 |
|
missing |
1.2 |
0.9 |
1.1 |